Quality management and quality assurance
The following definition of quality management is taken from the quality standard DIN EN ISO 9000:2005. This standard provides internationally recognized and clear definitions of the terms. It defines a quality management system as “that part of an organization’s management system that focuses on achieving results in relation to quality objectives in order to meet, as far as appropriate, the needs, expectations and requirements of interested parties”. A quality management system is therefore essentially responsible for ensuring that customer requirements are met. Many factors such as employees, processes, machines and information must be taken into account, coordinated and managed. The task of the quality management system is to integrate these factors into a consistent system so that they can be successfully designed and managed within the company. In line with the meaning of the word prevention, preventive quality management can be defined as a “management system for fulfilling customer requirements with the intention of preventing the non-fulfilment of customer requirements and identifying and eliminating errors or deviations as early as possible”. According to DIN EN ISO 9000:2005, a quality management system has three core elements: quality planning, quality assurance and quality control, which are explained below.
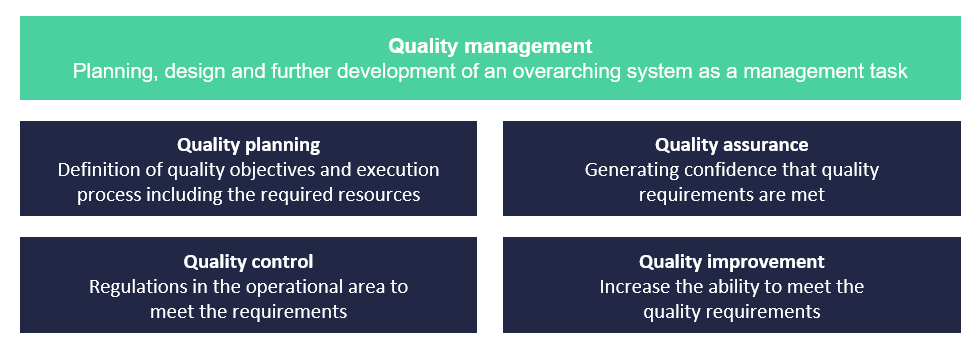
Quality planning
Quality planning is defined as “part of quality management that is aimed at defining the quality objectives and the necessary execution processes as well as the associated resources to fulfill the quality objectives”. The instruments of quality planning are known as quality methods. The best known of these are the two methods of Advanced Product Quality Planning and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). Quality planning includes planning with regard to the product (identification and prioritization of quality characteristics, definition of quality objectives, quality requirements and limiting conditions), planning with regard to management and execution activities (definition of quality objectives for manufacturing processes, testing and measuring equipment and process capability) as well as the creation of QM plans and the provision of quality improvement. Quality planning is therefore the definition of quality objectives, consistent risk assessment and the qualification of products and processes.
Quality assurance
According to DIN EN ISO 8402, 1995-08, section 3.5, quality assurance is any planned and systematic activity that is carried out within the QM system and is designed to create confidence that a unit will meet the quality requirement. Quality assurance is therefore the sum of all measures to ensure consistent product quality. A distinction is made between self-monitoring and external monitoring. Known methods in the context of quality assurance are classic testing with the help of testing and measuring equipment, statistical process control (SPC) and the analysis, prioritization and elimination of errors. Quality assurance is therefore the sum of all measures to ensure consistent product and process quality from the customer’s perspective.
Quality control
Quality control is the part of quality management that is aimed at fulfilling quality requirements. Quality control encompasses work techniques and activities both for monitoring a process and for eliminating the causes of unsatisfactory results. Quality control measures and quality assurance measures are interrelated. Quality control thus includes all work techniques and activities for analyzing a process and eliminating the causes of defects. Based on the definition of quality used in this thesis, the overriding goal of preventive quality management is understood to be sustainable quality improvement in the sense of higher product and process quality.
